end-tidal co2 monitoring non intubated patients
Defined as the monitoring of exhaled carbon dioxide through the respiratory cycle Measuring of End tidal CO2 is considered a standard of care for confirming endotracheal tube placement An important adjunct for assessing a critical patient The Journey of A Molecule Through the Respiratory Cycle. End tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in spontaneously breathing nonintubated patients.

Handheld Etco2 End Tidal Co2 Monitor For Patient Monitoring Co2 Spo2 China Capnography Monitor Handle Patient Monitor Made In China Com
Although the standard of care in ETC02 is well established for intubated patients there has been little emphasis on the use of capnography in nonintubated patients till now.
. End tidal co2 monitoring nursing considerations Thursday March 24 2022 In ETCO 2 monitoring a photodetector measures the amount of infrared light. 1 surveillance et monitoring of the intubated patient. End-tidal capnography provides reliable ventilatory monitoring for non-intubated patients presenting after sedative overdose to the emergency department.
4 achieving normocapnia in intubated head. Capnography can be used to assess unresponsive patients ranging from those are actively seizing to victims of chemical terrorism. Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO 2 in respiratory gases.
38 302306 2010. Of ventilator and also in non-ventilated patients. Waveform and end -tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 values.
3 monitoring of a patient in cardiac arrest. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
1 although commonly used in intubated patients receiving mechanical ventilation this technique is sometimes used in non-intubated patients. Understanding End Tidal CO 2 Monitoring. End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output.
When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a. In intubated patients this technique is adversely af fected by an elevated dead space to tidal volume ra tio VO VT leading to underestimation of arterial values33 The PETC02inaccuracy related toincreased VOVT may be exacerbated when monitoring non intubated individuals especially during sleepP. Monitoring respiratory status using end tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 which reliably reflects arterial PaCO 2 in intubated patients under general anesthesia has often proven both inaccurate and inadequate when monitoring non-intubated and spontaneously breathing patients.
The presence of a normal waveform denotes a patent airway and spontaneous breathing. Of distal end-tidal CO 2 capnography in intubated. Monitoring end-tidal CO 2 ET-CO 2 provides instantaneous information about ventilation how effectively CO 2 gas is being exhaledeliminated by the respiratory system perfusion how effectively CO 2 is being transported through the vascular system to the lungs and metabolism how effectively CO 2 is being produced by cellular metabolism.
The Intensive Care Society guidelines include ETCO 2 monitoring as one of the objective standards required for monitoring patients in transport and the American Heart Association recommends that all intubations must be confirmed by some form of ETCO 2 measurement. End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is the non-invasive measurement of exhaled CO 2. Norm al EtCO2 levels 46 to 60 kPa signify adequate perfusion.
Two common methods of non-invasive CO2 monitoring are end-tidal and transcutaneous. In addition to confirming the placement of the endotracheal tube and monitoring the tube. We conclude that measuring the end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure through a nasal cannula using the NBP-75 microstream capnometer provides an estimation of arterial carbon.
Procedural ventilation monitoring non intubated During cardiac arrest for quality of compressions and return of spontaneous circulation. A retrospective observational study examining the admission arterial to end-tidal carbon dioxide gradient in intubated major trauma patients. End-tidal capnography provides reliable ventilatory monitoring for non-intubated patients presenting after sedative overdose to the emergency department.
End tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 is the maximum expired carbon dioxide concentration during a respiratory cycle. Intubation and ETT placement. The measuring of expired CO 2 at the mouth has solicited growing clinical interest among physicians in the emergency department for various indications.
The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Rather than taking endless blood samples if the patient has an ETT or trache then capnography will provide end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2. Measurement of end-tidal CO2 therefore requires.
2 verification of the correct positioning of an endotracheal tube. Emerg Med Australas 2020. Fearon DM Steele DW.
Sidestream devices can monitor both intubated and non-intubated patients while mainstream devices are most often limited to intubated patients. A clinical comparison between conventional sidestream and microstream capnometers. The graphical representation of EtCO 2 is shown in a waveform format and is known as a capnogram.
This is particularly important in patients undergoing procedural sedation eg endoscopy colonoscopy. Position during transport capnography can provide qualitative and quantitative. The mean difference between the arterial to end-tidal carbon dioxide tension gradient measured in intubated and non-intubated spontaneously breathing patients was 1 - 6 mmHg CI95.
The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory. 9 10 Sidestream measurement has been the most common type of ETCO 2 measurement modality in Canadian facilities even as a number of new innovative and ultraportable mainstream capnography devices are becoming available.
An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable sensitivity 71-91 and specificity 94-100 for fluid responsiveness in two studies of patients breathing passively on the ventilator. The microstream capnometer provides a more accurate end tidal CO2 partial pressure measurement in nonintubated spontaneously breathing patients than conventional sidestream capnometers.
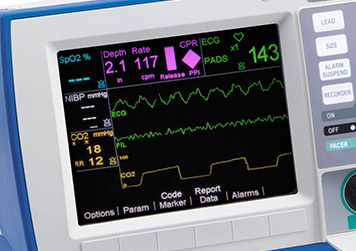
End Tidal Co2 Etco2 Capnography For R Series Zoll Medical
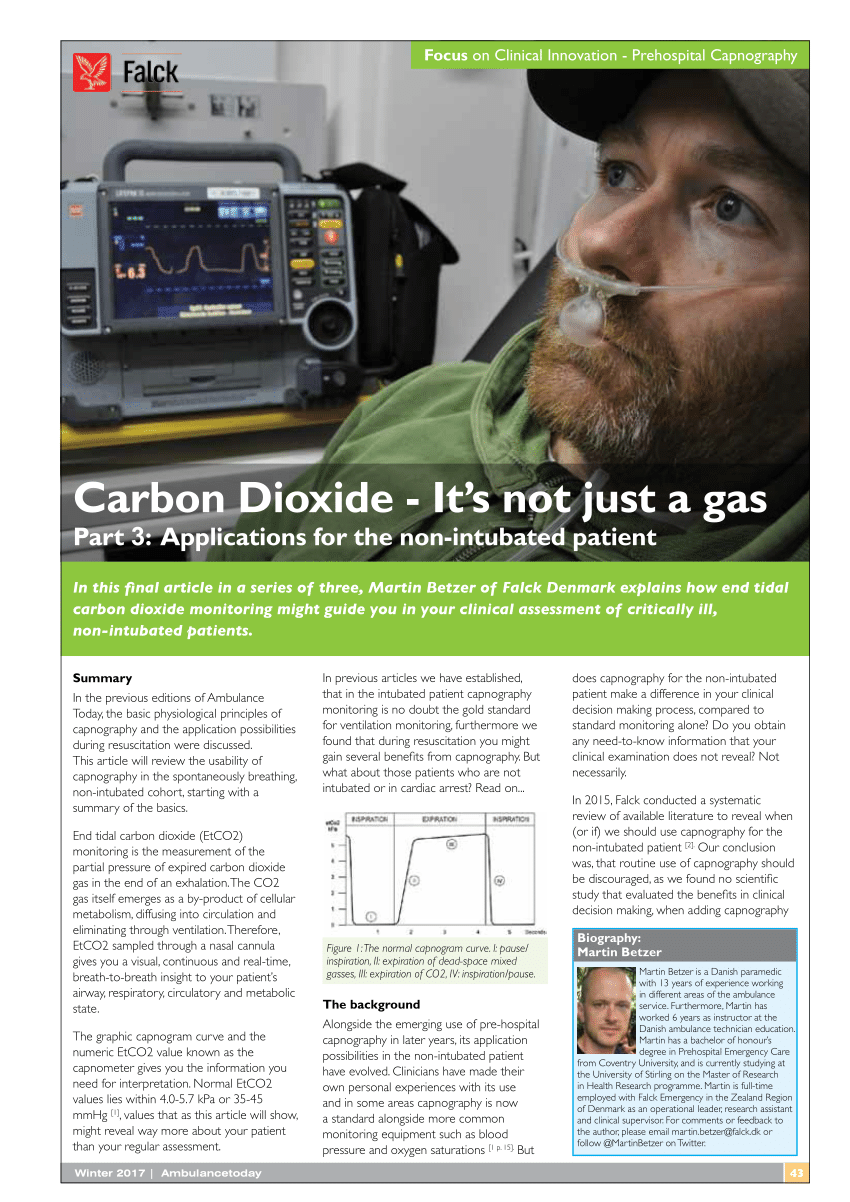
Pdf Capnography Its Not Just A Gas Applications In The Non Intubated Patient

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation
End Tidal Co2 Monitors Infinium Medical
End Tidal Co2 Monitor Etco2 Capnography
End Tidal Co2 Device Infinium Medical

The Critical Role Of Capnography Bound Tree

Philips Respironics Loflo End Tidal Co2 Kit Medys Medical Equipment And Accessories
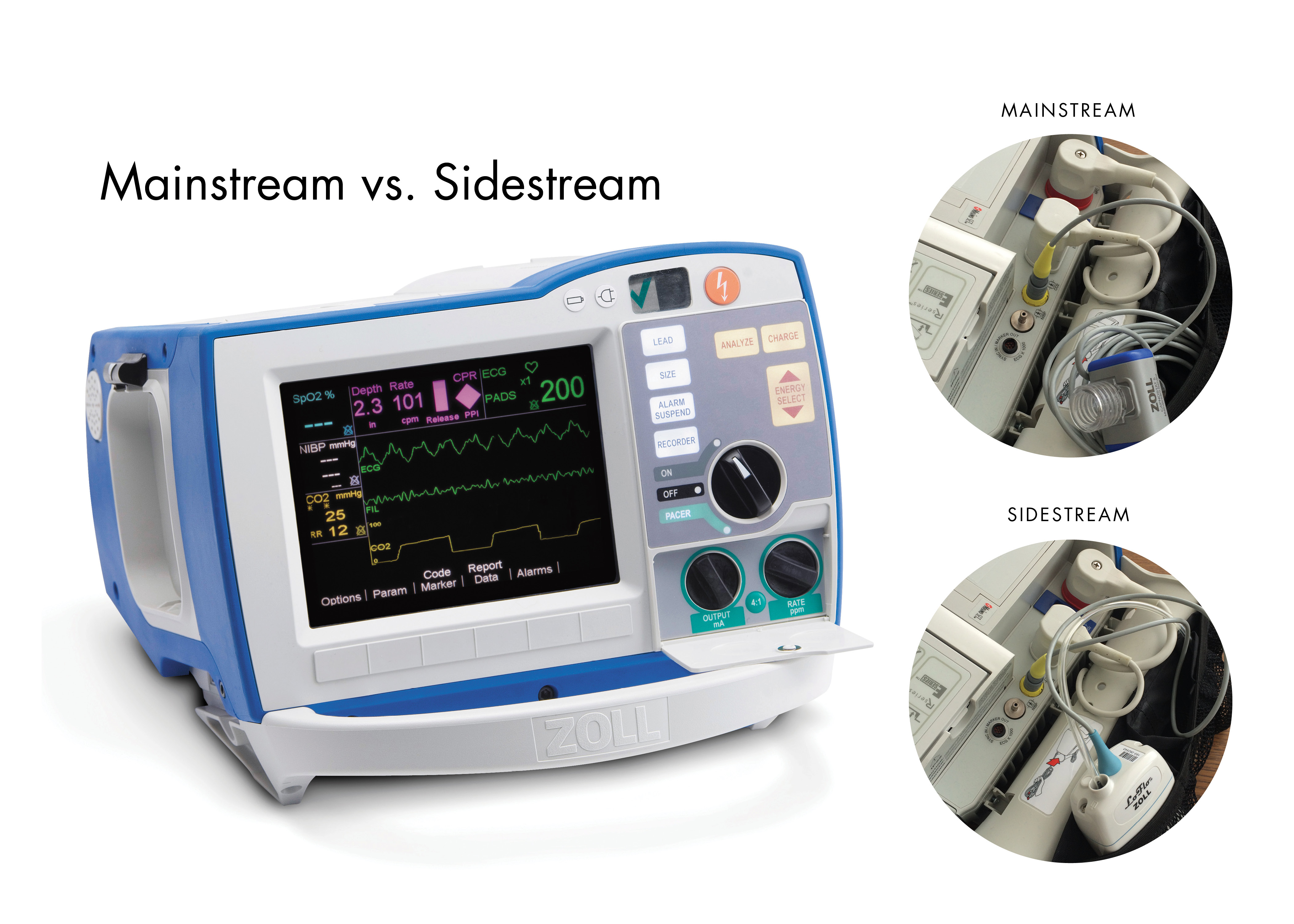
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical

Handheld Etco2 End Tidal Co2 Monitor For Patient Monitoring Co2 Spo2 China Capnography Monitor Handle Patient Monitor Made In China Com

End Tidal Co2 Micro Capnograph

Monitoring Capnography Helps Prevent Respiratory Complications Daic

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

How To Read And Interpret Capnography Waveforms Infinium Medical

Capno 101 How Does Capnography Work Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

End Tidal Co2 Emergency Nursing Icu Nurse Critical Care Emergency Medical Technician

